Different Types of Financial Institutions and Their Complete Details
Introduction of Financial Institutions
In the current economic climate, financial institutions are crucial because they offer crucial services that help the movement of capital and money. These organizations act as a middleman between savers and borrowers, assisting consumers, companies, and governments in managing their finances. We shall examine the various kinds of financial institutions, their roles, and their effects on the world economy in this article.
Commercial Banks Financial Institutions
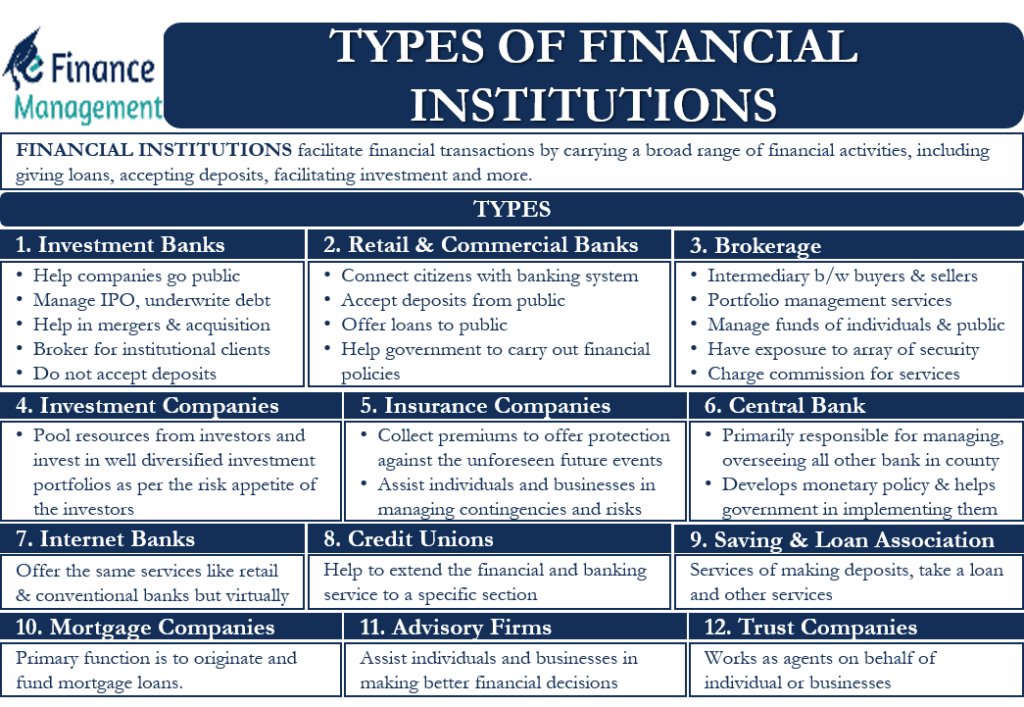
Perhaps the most well-known kind of financial institution is a commercial bank. They serve as the backbone of the financial system and provide a variety of services, including checking and savings accounts, loans, and mortgages. These banks serve as financial middlemen by taking client deposits and giving borrowers credit. Additionally, commercial banks offer a range of financial goods like credit cards, CDs, and foreign exchange services.
Investment Banks Financial Institutions
Particularly in the area of capital markets, investment banks play a critical role in the facilitation of complicated financial transactions. Underwriting stock and bond transactions, helps firms raise funds. Additionally, investment banks offer consulting services, knowledge in mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and trading in a range of financial instruments. They don’t often accept public deposits like commercial banks do.
Savings and Loans Associations
Savings and loan organizations, also referred to as S&Ls or thrifts, are primarily focused on giving homebuyers mortgage loans. They have traditionally focused on providing lengthy, fixed-rate mortgages. Their offerings have grown over time to include various consumer loans and savings accounts. S&Ls frequently operate closer to home than commercial banks.
Credit Unions Financial Institutions
Credit unions are non-profit financial cooperatives that are member-owned. They provide savings accounts, loans, and other financial goods to meet the demands of their members on a financial level. In comparison to commercial banks, credit unions often provide more palatable interest rates on savings accounts and loans. A credit union’s membership is frequently determined by shared ties, such as a job, place of residence, or membership in a particular group.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are financial instruments that aggregate the funds of numerous investors to buy a variety of stocks, bonds, and other securities. They are overseen by qualified fund managers who act as investors’ representatives while making investment decisions. Individual investors have access to professionally managed, diversified investment portfolios through mutual funds.
Insurance Companies
Financial institutions that offer protection against various dangers include insurance firms. A variety of insurance products are available from them, including life, health, vehicle, and property insurance. In exchange for policyholders paying premiums, insurance firms agree to provide payments in the event of insured losses. Additionally, they make premium investments to get returns.
Brokerage Firms
Trading in assets on financial markets is made easier by brokerage firms. They serve as a bridge between investors and over-the-counter marketplaces or stock exchanges. Brokerage companies provide a range of services, including as trading in stocks and bonds, investment research, and financial advising services. They can serve various sorts of investors as full-service or low-cost brokerages.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are private investment companies that use a variety of investing methods, frequently focusing on absolute returns, to provide profits for their investors. In contrast to mutual funds, hedge funds often have a more adaptable approach to investing and can employ leverage and derivatives to boost profits. They often have higher minimum investment requirements and are only open to accredited investors.
Private Equity Firms
Private equity firms specialize in buying out publicly traded corporations or investing in privately held businesses. They invest in, manage, and buy businesses with the intention of raising their value over time. To finance their acquisitions and investments, private equity firms rely on money from endowments, institutional investors, and high-net-worth individuals.
Venture Capital Firms
In return for stock ownership, venture capital firms finance start-ups and early-stage businesses. By providing capital to businesses with expansion potential, they play a critical part in fostering innovation and entrepreneurship. Venture capitalists frequently participate actively in the management of the businesses they fund, contributing not only to finance but also knowledge and resources.
Central Banks
Governmental organizations known as central banks are in charge of overseeing monetary policy, managing the banking industry, and controlling a nation’s money supply. They are essential for preserving price stability and economic expansion. During financial crises, central banks frequently have the power to act as lenders of last resort, set interest rates, and issue currency.
Conclusion
The backbone of the world economy is made up of financial institutions, which provide a wide range of services to meet the varied demands of people, companies, and governments. Every form of financial institution, from conventional commercial banks to cutting-edge hedge funds and venture capital firms, has a specific function within the financial system.


